
Astronomy is one of the world’s oldest studies of nature. The wonder and awe of astronomy are obvious when one stays up late to watch the stars, catch sight of a shooting star, or watch a comet shower.
Using either a telescope or binocular to view the stars is one of the ways to start. This article discusses the differences between these two tools. From magnification to portability, we bring forth the tools needed to shoot for the stars.
Astronomy is one of a few sciences in which amateurs play an active and significant role. Amateur astronomers have helped with several discoveries. Even though they aren’t specifically stargazing for research, some amateur astronomers make impressive contributions to citizen science. With the right equipment, nothing is out of reach, not even the stars.

“Astronomy for me is not just looking at the sky and enjoying it, but understanding why it is that we can see what we see,” said Sharon Morsink Trusted Source Sharon Morsink's Homepage A University of Alberta physicist who helped plan the observatory as CCIS was being built in 2005-2006 sites.ualberta.ca , An University of Alberta physicist who helped plan the observatory as CCIS was being built in 2005-06, “I love the fact that though the stars are so far away from us, we have come up with an understanding of them. It’s a thing of beauty when you can also explain what it is you see.”
Astronomy is the natural science that studies the stars. These include stars, moons, planets, nebulas, galaxies, comets, pulsars, radiation, cosmic radiation. If it can be seen in the night sky with a telescope or binoculars, it’s astronomy.
The human eye can see about 2,500 stars in the clearest of night skies. But usually, only about 1,500 to 2,000 stars can be seen due to weather, pollution, etc., and fewer still in night skies of cities due to the additional factor of city lights.
Unfortunately, using the naked eye isn’t as beneficial as using technology enhancements. That’s where equipment comes in to see better and farther.
What space objects can one see with a binocular?
Quite a few Solar System objects nearly invisible to the human eye are reasonably seen with binoculars. Within our solar system, binoculars can see larger craters on the Moon; Uranus, and Neptune; the “minor planets” of Ceres, Vesta, and Pallas; Titan, Saturn’s largest moon; and Jupiter’s Galilean moons.
Binoculars, otherwise known as field glasses, are one example of astronomy equipment. They are essentially two mini telescopes poot together to provide binocular vision (using two eyes instead of one).
| Pros |
Cons |
Binocular Vision
|
|
What space objects can one see with a telescope?
Telescopes come in a tremendous assortment of sizes, figures, and prices. This equipment is amazing at magnifying visibility on astronomical objects and events, including moons, planets, stars, galaxies, nebulae, and more.
Users recommend Celestron NexStar Telescope as one of the best for viewing planets, according to Astronomy Scope (Astronomy Scope: An online journal that publishes original research on Astronomy, Astrophotography, Stargazing & Equipment). It can locate nearly 40,000 objects using the patented technology.
| Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Telescopes and binoculars are similar in what they do but differ in how they do it and their aspects. Unlike binoculars that use provide binocular vision, a telescope provides monocular vision.
Both binoculars and telescopes provide a better image than the naked eye alone. That being said, telescopes will generally provide a more powerful and clearer image, but that’s not to say that they are better in all circumstances.
Magnification is created by the ratio of the focal length of the objective divided by the eyepiece’s focal length. A magnification of 7 produces an image 7 times larger than the original from that distance. A lower magnification provides a larger field of view which is helpful when viewing the milky way or large nebulous objects such as deep-sky objects, nebulae, and galaxies.
Each scope comes with a focal length, the distance between the main lens and the image it forms. Focal length is the number we often see printed, engraved, or marked on the scope, typically between 400 and 3,000 mm.
Magnification is typically the first number in the biovular descriptions (7X35, 8X50, 8X40, etc.). The second number is the objective diameter (7X35, 8X50, 8X40, etc.) which determines the image’s resolution. Binoculars range from 7 to 10 times, with some specialized binoculars reaching a range of 15 to 25 magnification.
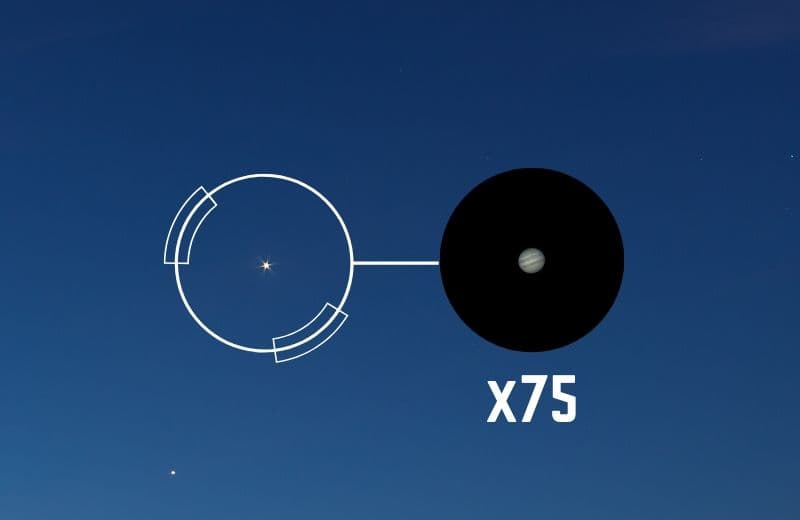
Of the binoculars, 10×42 binoculars are one of the best for astronomy because of their magnification”.
When compared with magnification, binoculars have an advantage because they provide low power and thus a wider field of view. On the other hand, Telescopes offer a greater advantage with their interchangeable eyepieces and image stability using the mounting platform.
Aperture is an important aspect of astronomy. It’s arguably the most important aspect. The aperture value of both a telescope and the binocular determines how bright the image is and how sharp the image is. This is because the diameter of the objective lens increases the total amount of light captured, increasing the magnification and clarity.
Compared to the human unaided eyes with a 7mm (0.28 inch) aperture at best, even a small telescope with a 70 mm scope provides 100 times as much light as the eye reveals amazing details and views.
The larger the aperture, the more impressive the viewed object will look. In general, binoculars are going to have smaller apertures than telescopes. Binoculars that are specifically designed for astronomical stargazing will have a larger aperture Trusted Source Aperture - Wikipedia In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. en.wikipedia.org , typically between 70 mm or 80 mm range.
Combining the benefits of a large telescope with the convenience of a binocular is the Barska Encounter Binoculars. According to most reviews, the Barska Encounter Binoculars are among the most sophisticated binoculars for celestial observations, offering multi-coated optics and high-quality BAK-4 prisms.
Both have focusing mechanisms to bring the image closer and clearer.
The binocular uses a center know or wheel to focus the image which the telescope has a focuser that has a steeper learning curve. Telescopes have a much steeper learning curve because there are many more moving parts and various things that can go wrong, such as backlash, slop, image shift, and much more.

Portability and size are important to consider depending on where one stargazes. Binoculars are extremely convenient for travel and use. The average weight of 42 mm and 50 mm models of binoculars can weigh anywhere between 21 oz to 35 oz. Yes, ounces. They’re that light.
Portability is vital in a telescope as binoculars are already inherently portable.
The average weight of a smaller 100 mm telescope is 19.9 lbs (9.0kg). Typically, the average weight per millimeter of telescope aperture is 0.199 lbs (0.090 kg). Telescopes with big lenses or mirrors tend to be heavier and bulkier, making them an inconvenience if one wants to travel with them or store them in a small space.
Travelling can be important to astronomy, especially with different locations providing different views and quality of views depending on the amount and degree of light pollution. For Example, a recent publication from Huria: Journal of the Open University of Tanzania explains that “Tanzania’s geographic location near the equator offers 95% of the view of stars Trusted Source Huria: Journal of the Open University of Tanzania Huria is an international journal that publishes original research papers of academic interest (theoretical, applied and general). www.ajol.info that can be seen in one night.”
That being said, traveling to Tanzania would require portability not only to get there but to travel and find the perfect spot. That being said, a telescope that could be used anywhere is vital. The editor’s choice at The Optic for portable telescopes is the Celestron Nexstar 6SE which provides Up to 354x useful magnification while being user-friendly.
Weatherproofing is important not only to the gear but also to the outcome of the search for stars.
“Anyone trying to make astronomical observations in the desert southwest during the summer thunderstorm season knows how futile that can be. For this reason, most observatories in the area do not fill their schedules during that time, focusing instead on the maintenance and engineering of telescopes and instruments. For our joint program with Apache Point Observatory (APO) to search for new trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs*), this means a few months of relatively quiet, if unproductive, time,” explains Gil Esquerdo of the Planetary Science Institute. Trusted Source Planetary Science Institute Anyone trying to make astronomical observations in the desert southwest during the summer thunderstorm season knows how futile that can be. www.psi.edu
Most telescopes have no waterproofing features at all, while most binoculars are water-resistant if not waterproof. Binoculars are designed to be durable and handle extreme temperature changes.
If one is going to invest in astronomy, we want it to be a durably buy.
Telescopes are fragile as they have many exposed optics and open tubes and lack the coating and waterproofing that binocular has. All combined, this is not a good mix when the terrain or environment is uncontrolled.
Binoculars are not as fragile as their counterpart. They are built to be durable with optical coatings, gas purges, fog proof protection, external lens coatings. They can handle a reasonable amount of abuse, dirt, drops and still function. More than that, most binoculars are treated to handle extreme temperature changes, as well as stray debris (dust, rain, wind, etc.)
Up to this point, the astronomy binoculars vs. telescope debate has been about the equipment itself but not its use. The logistics of astronomy require there to be an aspect of convenience for their equipment because of the need to travel. Aspects such as size, eyepieces, weight, length, durability impact the usability of the equipment.
While it’s tempting to go to extremes, either the cheapest or the most expensive option, it’s not the only aspect to consider. Astronomy binoculars and telescopes have more than just a price to contemplate.
Budgeting is important to make sure that one is not only getting a great tool but also getting a great deal. Telescopes can range from $200 to $8000, while binoculars can range from $50 to $1200. Many great telescopes are in the middle range and at only $500.
That being said, be sure to have finances left over for astronomer additions. Don’t underestimate the importance and benefit of detailed sky atlas, good guidebooks, filters, dew prevention, and additional stargazing gear.
Comparing binoculars to telescopes gives astronomers a range of equipment to choose from. Astronomy binoculars telescope is both valid tools to use to learn and study the night sky.
The conversation of telescope vs. binoculars comes down to the pros and cons of the individual user.
Now with this information, we are ready to shop. Don’t discount the benefit of local networking. Make sure to reach out to a local astronomy club to enhance the knowledge and contacts.





